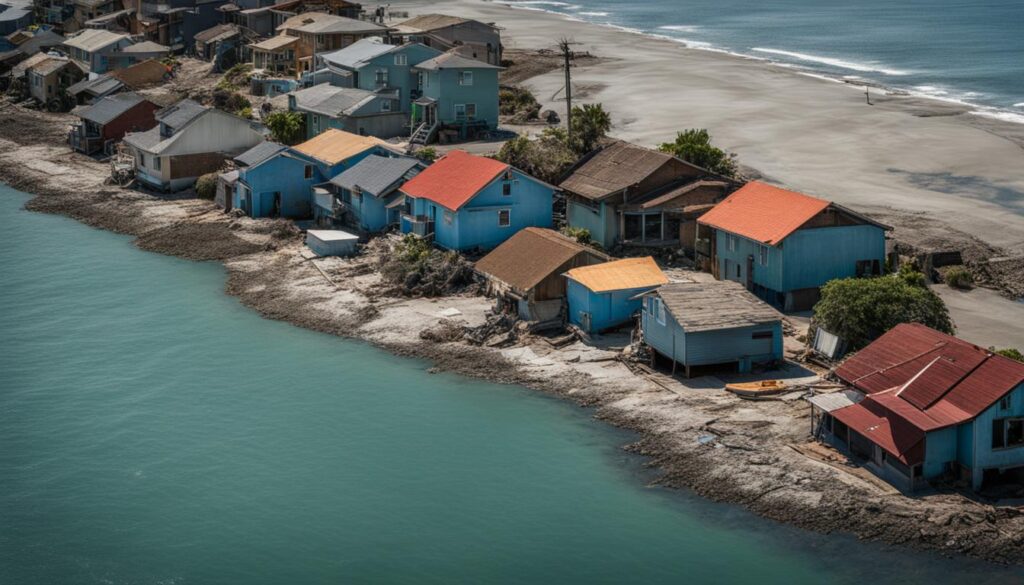

Climate change poses a significant threat to coastal communities, leading to the displacement of people due to various climate-related factors. Research indicates that the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, resource scarcity, and other climate change effects will result in large-scale human migration, particularly in developing countries. The impacts of climate change on migration include intensifying competition for resources, outbreaks of diseases, and increased stress on U.S. borders. Concrete data shows that climate change contributes to both sudden onset events, such as flooding and intensified storms, as well as slow onset events like desertification and sea-level rise.
The Pacific Islands serve as clear examples of climate change as the sole factor prompting migration, with rising sea levels leading to the loss of islands and the displacement of populations. South Asia and Northwest Africa are also experiencing migration patterns influenced by climate change, with increasing temperatures, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events exacerbating internal and international migration. The intersection of climate change and migration necessitates comprehensive solutions and legal frameworks to address the challenges faced by climate migrants. However, current international agreements are insufficient and lack legal obligations to support climate migrants, highlighting the need for new strategies to protect and assist those affected by climate change-induced migration.
Key Takeaways:
- Climate change is causing large-scale migration, particularly in developing countries.
- The impacts of climate change on migration include competition for resources and increased stress on U.S. borders.
- Both sudden and slow onset climate events contribute to migration patterns.
- The Pacific Islands, South Asia, and Northwest Africa are experiencing migration influenced by climate change.
- Comprehensive solutions and legal frameworks are needed to address the challenges faced by climate migrants.
The Impact of Climate Change on International Peace and Security
Climate change is not just an environmental issue; it is also a threat to international peace and security. The consequences of climate change, such as rising sea levels, resource scarcity, and forced migration, are leading to increased tensions and conflicts around the world. As nations compete for dwindling natural resources, disputes over access to water, land, and energy sources are becoming more frequent and intense.
One of the primary sources of conflict in a changing climate is sea-level rise. As coastlines disappear and land is lost to the ocean, nations are faced with the challenge of redefining their maritime boundaries and asserting control over remaining resources. This competition over natural resources can escalate into territorial disputes and even armed conflicts, as seen in recent conflicts in the South China Sea.
Forced migration and the displacement of populations are also significant consequences of climate change, exacerbating existing social and political tensions. As people are forced to leave their homes due to the impacts of climate change, they often find themselves in unfamiliar territories, competing for limited resources with the local population. This can lead to social unrest and even violence, as witnessed in regions like the Sahel and the Horn of Africa.
“The impact of climate change on international peace and security cannot be ignored. It is a global challenge that requires immediate attention and coordinated action from the international community.” – International Panel on Climate Change
Addressing the legal challenges posed by climate change-induced sea-level rise is another critical aspect of ensuring international peace and security. The loss of state territory due to rising sea levels raises questions about statehood and maritime boundaries, creating a complex legal landscape that requires new frameworks and agreements to navigate.
| Effects of Climate Change on Peace and Security | Examples |
|---|---|
| Competition over natural resources | Tensions in the South China Sea |
| Forced migration and displacement of populations | Violence in the Sahel and Horn of Africa |
| Legal challenges of sea-level rise | Loss of state territory and maritime boundary disputes |
As the impacts of climate change continue to intensify, it is crucial for the international community to acknowledge and address the link between climate change and peace and security. Proactive measures should be taken to mitigate the causes and consequences of climate change, promote sustainable development, and foster international cooperation to ensure a more peaceful and secure future for all.
The Future of Climate Change and Migration in the United States
The impact of climate change in the United States is becoming increasingly evident, with various environmental factors affecting the country’s communities. Rising temperatures, heatwaves, droughts, floods, and increased wildfires are all consequences of climate change that are leading to unprecedented challenges.
One of the significant impacts of climate change in the United States is the potential for population shifts due to climate influences. Research suggests that as the effects of climate change intensify, individuals and families may choose to relocate from areas that are particularly vulnerable to environmental risks. Heatwaves and declining environmental quality, for example, can make certain regions less habitable and prompt people to seek more favorable conditions elsewhere.
This migration, however, comes with its own set of economic and social consequences. As people move away from areas affected by climate change, there can be an economic strain on both the places they leave behind and the ones they move to. The shift in population can lead to changes in the labor market, housing demands, and social dynamics, which can have far-reaching effects on local communities.
The Economic and Social Consequences of Climate Migration
The economic consequences of climate migration can be twofold. On one hand, areas that experience a decline in population may face challenges in maintaining local businesses and infrastructure. This can lead to a decrease in economic opportunities and investment, potentially resulting in a downward spiral for the affected community.
On the other hand, areas that become destinations for climate migrants may face economic strains as well. The sudden influx of new residents can put pressure on housing, public services, and resources, which may not be adequately prepared to accommodate the increased demand. This can lead to rising costs, overcrowding, and strained social services.
“The impact of climate change on migration is not just an environmental issue—it’s a multifaceted challenge that requires comprehensive solutions and proactive policy-making.”
Moreover, the social consequences of climate migration cannot be overlooked. Displacement and the disruption of established communities can lead to social instability, strained social cohesion, and increased vulnerability, particularly among those who are already marginalized or disadvantaged.
The future of climate change and migration in the United States requires focused attention, robust policy frameworks, and coordinated efforts to mitigate the immediate and long-term effects. By addressing the economic and social consequences of climate migration, policymakers can work towards creating sustainable solutions that protect both the environment and the well-being of communities affected by climate change.
Section 4: Conclusion
As the impacts of climate change become more apparent, individuals and communities are facing the difficult decision of whether to relocate. The increasing awareness of climate risks and the undeniable impact of climate change on communities are driving a shift towards proactive policy-making.
People are starting to recognize the urgent need to adapt and protect themselves against the effects of climate change. The realization that climate change will bring profound transformations to their lives has spurred a prioritization of climate as a key political issue.
However, the challenges of climate migration are complex and multifaceted. Policymakers must carefully weigh the potential impacts and make difficult choices about which communities to protect. As the effects of climate change continue to unfold, it is crucial to take action to safeguard vulnerable populations and create sustainable solutions for the future.
Proactive policy-making is essential to address the challenges of climate migration effectively. By implementing comprehensive strategies and legal frameworks, societies can work towards ensuring the well-being of those affected by climate-induced relocation decisions. The time to act is now, as we strive to build a resilient and sustainable future for all.
FAQ
What are the main impacts of climate change on migration?
The impacts of climate change on migration include intensifying competition for resources, outbreaks of diseases, and increased stress on U.S. borders.
Which regions are experiencing migration patterns influenced by climate change?
The Pacific Islands, South Asia, and Northwest Africa are experiencing migration patterns influenced by climate change, with rising sea levels, increasing temperatures, and extreme weather events exacerbating internal and international migration.
How does climate change contribute to migration?
Climate change contributes to both sudden onset events, such as flooding and intensified storms, as well as slow onset events like desertification and sea-level rise. These changes can lead to the loss of islands, displacement of populations, and the need for migration.
What legal protections exist for climate migrants?
Current international agreements lack legal obligations to support climate migrants, highlighting the need for new strategies and comprehensive solutions to protect and assist those affected by climate change-induced migration.
How does climate change impact international peace and security?
Rising sea levels, disappearing coastlines, and scarce resources are leading to tensions and conflicts around the world. Changes in baselines and maritime zones due to sea-level rise provoke increased competition over natural resources, force migration, and displace populations, posing legal challenges for international law.
How does climate change affect the United States?
Climate change is expected to lead to a decline in environmental quality, characterized by increased heat and reduced water availability. Approximately half of the U.S. population, or 162 million people, are likely to experience these impacts, with an estimated four million Americans potentially living in areas unsuitable for human life by 2070.
What are the economic and social consequences of climate migration in the United States?
Climate migration is projected to increase poverty and exacerbate existing inequalities, leading to economic challenges and social instability. The cost of maintaining current infrastructure and defending vulnerable areas against climate threats is proving to be unaffordable, forcing difficult choices about which communities to save and which to sacrifice.
How is awareness of climate change impacting relocation decisions?
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events and rising temperatures are raising awareness of the need to adapt and protect against climate risks. Americans are prioritizing climate as a key political issue and policymakers are faced with the task of making choices about which communities to protect and how to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
What needs to be done to address the challenges of climate migration?
Proactive policy-making is crucial to address the challenges of climate migration and ensure the well-being of affected communities. Comprehensive solutions and legal frameworks are needed to protect and assist climate migrants.
MORE SOURCES TO READ:
- https://press.un.org/en/2023/sc15199.doc.htm
- https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/09/15/magazine/climate-crisis-migration-america.html
- https://www.brookings.edu/articles/the-climate-crisis-migration-and-refugees/
![]()








Recent Comments