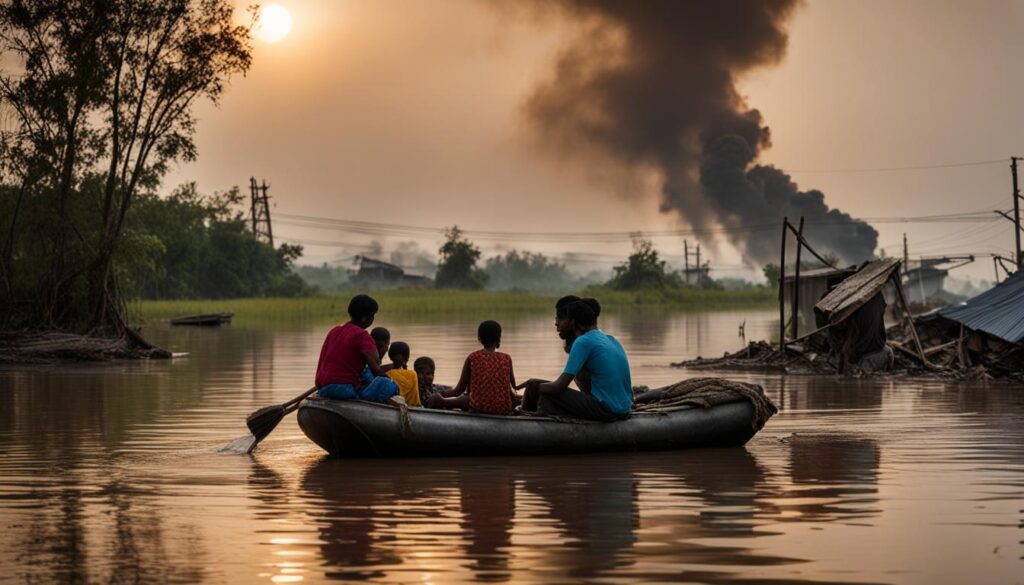

Climate change is an urgent global issue that is causing the displacement of populations worldwide. The United Nations has reported that achieving the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030 is highly unlikely due to the magnitude of extreme poverty, inequality, and environmental catastrophes threatening our future. Additional funding of $33.6 trillion over the next eight years is needed to address the climate emergency.
Climate change has already had a significant impact on vulnerable nations, including Zimbabwe and countries in Central America, leading to the displacement of people. In 2020, Cyclone Amphan in Bangladesh alone resulted in 500,000 families losing their homes. The effects of climate change, such as flooding, hurricanes, and droughts, are expected to continue contributing to the displacement of populations globally.
Key Takeaways:
- Climate change is causing the displacement of populations worldwide.
- Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030 is highly unlikely due to environmental catastrophes.
- An estimated $33.6 trillion is needed over the next eight years to address the climate emergency.
- Vulnerable nations, like Zimbabwe and countries in Central America, are already experiencing significant displacement.
- Climate-related disasters, such as Cyclone Amphan in Bangladesh, have led to the loss of homes for many families.
The Nexus between Climate Change and Displacement
Climate change is not only impacting our environment but also causing widespread displacement around the world. The relationship between climate change and forced migration is complex and multifaceted. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has identified several key impacts that highlight the urgent need to address this issue.
One significant impact is the reduced availability of water in certain regions, leading to water stress and droughts. This is particularly evident in parts of Africa and the Mediterranean, where communities are at risk of water scarcity and its devastating consequences. Additionally, the decrease in crop yields, mainly in Africa, poses an increased risk of hunger for millions of people. The vulnerability of densely populated coastal areas to rising sea levels is another critical concern, as it can result in the displacement of tens of millions of individuals in Asia and Africa.
The overall impact of climate change on health is projected to be negative, especially for marginalized communities. The increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and heatwaves, put vulnerable populations at greater risk. These impacts highlight the urgent need to address the nexus between climate change and forced migration.
Addressing the Link between Climate Change and Forced Migration
Recognizing the link between climate change and displacement is crucial in developing effective strategies to mitigate its impact. International cooperation and collaboration are key to addressing this global issue. Governments, organizations, and individuals must work together to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable development, and support vulnerable communities.
“Climate change knows no borders and affects us all. We must come together to find solutions and protect those who are most affected by its consequences.” – Climate Activist
By investing in renewable energy, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, and implementing resilient infrastructure, we can mitigate the effects of climate change and reduce displacement. Additionally, providing financial support and compensation to affected communities is vital in ensuring their resilience and recovery.
Conclusion
The nexus between climate change and forced migration calls for urgent action. Understanding and addressing the impacts of climate change is crucial in protecting communities and ensuring a sustainable future for all. By working together and taking meaningful steps, we can minimize the human and environmental costs of climate-related displacement and build a more resilient world.
The Human and Financial Costs of Climate-Related Disasters
The year 2022 has witnessed the devastating impact of climate-related disasters, both in terms of human lives and financial burdens. According to a report by Christian Aid, the toll of these disasters has been staggering, with the 10 most expensive storms, floods, and droughts alone costing at least $3 billion each. Among these, Hurricane Ian stands out as the costliest, resulting in a financial impact of $100 billion, claiming 130 lives, and displacing over 40,000 people in the United States and Cuba.
Pakistan faced the wrath of the climate crisis with the devastating floods, claiming the lives of 1,739 individuals and displacing a staggering 7 million people. The estimated costs of this disaster exceed $30 billion, underscoring the profound impact of climate change-induced migration. As the floods ravaged communities and homes, their consequences reverberated far beyond the immediate aftermath, leaving a trail of destruction that will require substantial resources to rebuild and rehabilitate.
Other parts of the world have also experienced the destructive power of climate-related disasters. Storms wreaked havoc in the United Kingdom and Europe, while floods brought devastation to Malaysia and Brazil. Droughts inflicted suffering upon China and Brazil, and heatwaves tormented India and Pakistan. The toll on human lives and livelihoods cannot be overstated, necessitating urgent action to mitigate the effects of climate change and find sustainable solutions to the resulting displacement of populations.
The report from Christian Aid echoes the call for international cooperation and financial compensation to support those affected by climate-related disasters. By working together, the global community can provide vital assistance to displaced populations and allocate resources to rebuild shattered lives. It is only through collective efforts and a shared commitment to addressing the root causes of climate change that we can shape a more resilient future for vulnerable communities impacted by these devastating events.
FAQ
What is climate-induced displacement?
Climate-induced displacement refers to the forced migration of people as a result of the impacts of climate change. It occurs when environmental catastrophes, such as floods, droughts, and storms, make living conditions uninhabitable or unsustainable.
How does climate change lead to displacement?
Climate change contributes to displacement through various mechanisms. This includes rising sea levels, leading to the loss of coastal land and the displacement of communities. Additionally, extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods, can destroy homes and infrastructure, forcing people to flee their homes.
Which regions are most affected by climate-induced displacement?
Vulnerable nations in regions such as sub-Saharan Africa, Central America, and Asia are particularly affected by climate-induced displacement. These regions are prone to extreme weather events and face challenges related to water scarcity, crop failure, and rising sea levels.
How does climate change affect health and well-being?
Climate change has a negative impact on health, especially for marginalized communities. It contributes to the spread of vector-borne diseases, increases the risk of malnutrition and food insecurity, and exacerbates mental health issues due to the trauma of displacement and loss of livelihoods.
What are the financial costs of climate-related disasters?
Climate-related disasters have significant financial costs. Storms, floods, and droughts in 2022 alone resulted in billions of dollars in damages. The cost of these disasters includes the expenses associated with rebuilding infrastructure, providing emergency aid, and supporting displaced populations.
How can international cooperation help address climate-induced displacement?
International cooperation plays a crucial role in addressing climate-induced displacement. By working together, countries can share resources, knowledge, and expertise to develop strategies for mitigating climate change and supporting displaced populations. Financial compensation and aid can also help affected communities recover and rebuild their lives.
MORE SOURCES TO READ:
- https://press.un.org/en/2022/gashc4357.doc.htm
- https://www.brookings.edu/articles/displacement-caused-by-the-effects-of-climate-change-who-will-be-affected-and-what-are-the-gaps-in-the-normative-framework-for-their-protection/
- https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2022/dec/27/biggest-climate-toll-in-year-of-devastating-disasters-revealed
![]()









Recent Comments